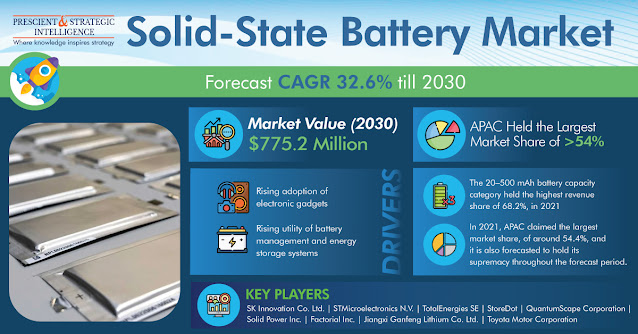
The solid-state battery industry has garnered $61.3 million revenue in 2021, and it is expected to generate $775.2 million revenue in 2030, rising at a rate of 32.6% from 2021 to 2030. The growing adoption of electronic gadgets, rising road traction of electronic vehicles, and growing utility of energy storage systems and battery management propels the industry growth.
Solid-state batteries provide support in combating the problems with batteries with liquid electrolytes, such as leakage or corrosion at the electrodes, which involve the usage of solid electrolytes with ionic conductivity to restrict the ohmic drop at electrodes.
In this manner, the lithium-conducting chalcogenide glasses serve as excellent candidates with 10 to 100 times larger conductivity compared to their oxide counterparts.
Several solid-state batteries consist of lithium-conducting chalcogenide glass or glass-ceramic with the development of solid electrolytes.
In addition, the increasing R&D activities on solid-state batteries, growing IoT-based systems adoption, and electronic device miniaturization fuel the industry's growth.
The battery capacity of 20-500 mAh captures the largest revenue share, accounting for 68.2% in 2021. It is led by solid-state battery applications, such as domestic appliances, wearable medical devices, and energy storage systems. Which need such variants.
Why do we need a solid-state battery?
We need a solid-state battery to boost the capacity of electric vehicle batteries. It is predicted that electric vehicles will replace internal combustion engine vehicles, and lead the auto industry. Thus, EVs are required to deliver a similar mileage level, as the current ICEV. Therefore, it is crucial to expand the capacity of the electric vehicle battery.
There are two methods for increasing the capacity. The first method involves expanding the number of batteries. In this method, if the battery price rises, batteries capture a lot of vehicle space.
A solid-state battery possesses higher energy density compared to a Li-ion battery that utilizes a liquid electrolyte solution. A solid batter does not pose any risk of fire explosion. It does not require any safety components, and thus captures lesser space. Hence, there is enough space left for more active materials that expands the batter capacity.
Therefore, the growing road traction of electric vehicles propels the demand for solid-state batteries.








No comments:
Post a Comment